GST for Small Businesses: A Complete Guide from Registration to Filing
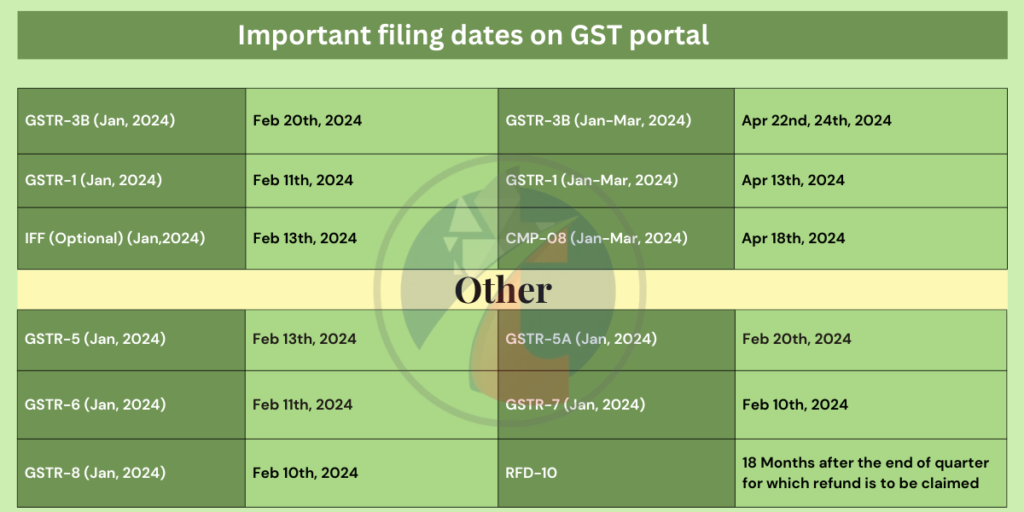
What is GST? The Goods and Services Tax (GST), introduced on July 1, 2017, is one of India’s biggest tax reforms.It replaced the old maze of indirect taxes like VAT, service tax, and excise duty with a single, unified tax system.GST is levied on the supply of goods and services, creating a common national market and simplifying compliance. For small businesses, GST is not just another tax formality—it’s a gateway to growth and recognition.Under the earlier system, businesses had to deal with multiple tax departments and state-specific rules,often leading to confusion and extra costs. GST changed that by eliminating the “tax-on-tax” effect andmaking the entire process more transparent, digital-first, and business-friendly. Most importantly, GST registration helps small businesses build trust. It signals professionalism and compliance,opening doors to partnerships with larger companies, government contracts, and expansion into new markets.In short, GST is more than a tax—it’s a step toward becoming a recognized and competitive player. Why GST Matters for Small Businesses GST has transformed the way small enterprises operate. Here’s why it’s a game changer: – Market Expansion – Earlier, selling in another state required multiple registrations and approvals. With GST, businesses can sell anywhere in India without unnecessary hurdles. – Stronger Business Credibility – A GST-registered business is seen as reliable. Many corporate buyers and suppliers prefer GST-compliant vendors since it allows them to claim input tax credit. – Simplified Compliance – Instead of filing multiple returns under different tax laws, businesses now deal with just one tax—GST. – Improved Competitiveness – By removing the cascading effect of taxes, GST lowers costs, allowing small businesses to price their products more competitively. 👉 In essence, GST is not just about tax compliance—it’s a tool that empowers small businesses to grow, expand, and stay competitive. Understanding GST Structure in India Types of GST – CGST, SGST, IGST, and UTGST The GST system is designed to balance revenue between the Centre and the States. Here’s how it works: – CGST (Central GST): Collected by the central government on transactions within a state. – SGST (State GST): Collected by the respective state government on intra-state sales. – IGST (Integrated GST): Collected by the central government on inter-state transactions. – UTGST (Union Territory GST): Applied to sales within union territories. Example: If a Delhi-based business sells to a customer in Delhi, CGST + SGST apply. If the same business sells to a customer in Mumbai, IGST applies. GST Tax Slabs and Their Impact on Small Enterprises To simplify compliance and reduce confusion, the government has moved from a multi-slab system to a two-slab GST structure,along with a special high rate for certain goods. – 5% GST – Essentials and Merit GoodsEveryday necessities such as packaged food, household items, and services that affect the common man fall under this slab.Many items previously taxed at 5% and 12% have now been shifted to this lower 5% rate. For small businesses, this meanshigher affordability for customers and stronger demand. – 18% GST – Standard Goods and ServicesThis is now the default GST rate. It covers manufactured goods, electronics, garments, and professional services.Items earlier taxed at 18% and most of the 28% category have been moved here. For small enterprises, this brings stability,predictability in pricing, and smoother ITC claims. – 40% GST – Luxury and Sin Goods (Special Category)Certain high-end or harmful products such as tobacco, pan masala, and ultra-luxury cars fall into this bracket.While most small businesses won’t be affected, it’s relevant for niche industries. Impact on Small Businesses:This simplified structure makes compliance far easier. Instead of juggling five tax rates, small businesses now justfocus on 5%, 18%, or 40% (special category). This reduces paperwork, minimizes errors, and lowers the risk of penalties.Many small traders will also benefit from lower prices, especially if their products previously fell in the 12% or 28%slabs but are now down to 5% or 18%. GST Registration for Small Businesses Who Needs to Register Under GST? Not every small business must register under GST. Registration is mandatory if: – Your annual turnover exceeds ₹40 lakhs (for goods) or ₹20 lakhs (for services).– You sell through e-commerce platforms like Amazon or Flipkart (mandatory regardless of turnover).– You make inter-state sales.– You operate as a casual taxable person (temporary business in another state).– You are liable to pay reverse charge tax. 👉 Even if your turnover is below the limit, voluntary registration can be beneficial.It enhances credibility and allows you to claim input tax credit. Step-by-Step Process for GST Registration Documents Required for Registration – PAN card of the business/owner– Aadhaar card of proprietor/partners/directors– Proof of business registration or incorporation– Address proof (electricity bill, rent agreement, etc.)– Bank account details (cancelled cheque or statement)– Digital Signature Certificate (DSC) of the authorized person Once registered, businesses can issue GST invoices, claim ITC, and expand operations legally across India. GST Compliance for Small Businesses GST Return Filing Basics Once you’re registered, filing GST returns becomes a regular responsibility. Returns are filed to declare sales,purchases, and tax liability. Depending on turnover, returns may be monthly, quarterly, or annually. Filing GST returns on time is vital because it:– Maintains compliance and avoids penalties.– Enables businesses to claim input tax credit (ITC).– Ensures smooth cash flow. Non-compliance, on the other hand, can result in hefty penalties, late fees, and even cancellation of registration. Different Types of GST Returns – GSTR-1 – Details of outward supplies (sales).– GSTR-3B – Summary of sales, purchases, and tax liability.– GSTR-4 – For businesses under the composition scheme.– GSTR-9 – Annual return.– GSTR-9C – Reconciliation statement for larger businesses. 👉 For most small businesses, the key returns are GSTR-1 and GSTR-3B. Missing these filings can block ITC claims and attract penalties. Common Mistakes in GST Filing (and How to Avoid Them) – Incorrect GSTIN – Always double-check before filing.– Wrong classification of goods/services – Use correct HSN/SAC codes.– Not reconciling purchase data – Ensure invoices match supplier records.– Missing deadlines – Use reminders or GST software to stay on track. 💡 Small businesses can
GST for Small Businesses: A Complete Guide from Registration to Filing Read More »